The Ultimate Guide to Managing Data Subject Requests
October 6, 2021
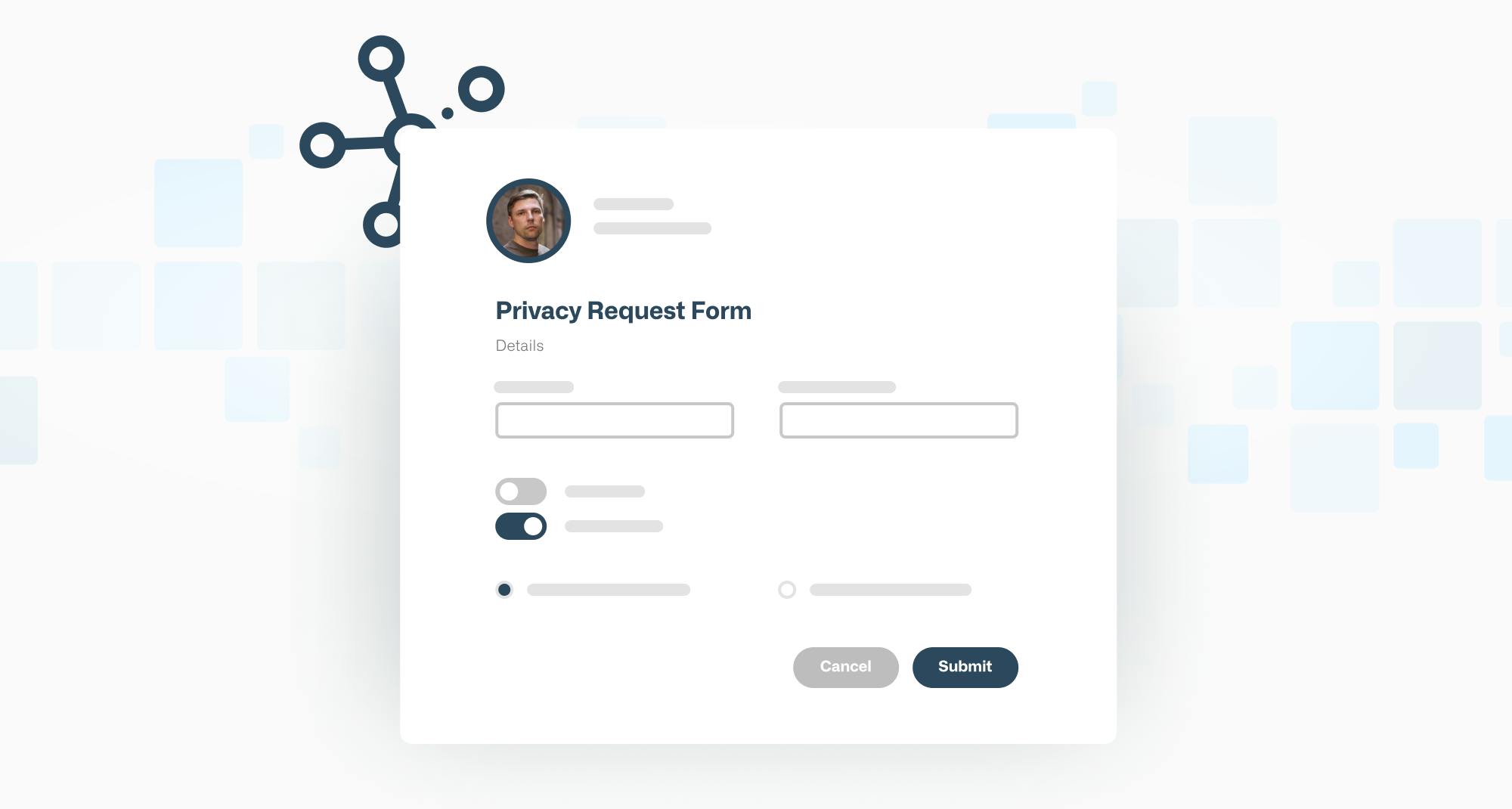
A driving force behind data privacy legislation around the globe is the shift in control of data from big tech to the individual. At the core of emerging legislation is a concept called “data subject requests”, or in the US, often referred to as "privacy requests".
Consumers are increasingly aware of these rights being written into law. These rights are in place so individual can protect their data, and extend to allowing them to control how much (or any) personal data a given organization might have on them. In short, these rights allow an individual or consumer to go to virtually any business and request their personal data be deleted from the organization's systems, or ask for a downloadable copy of it.
In this article, we cover data subject requests in detail and how to operationalize the process within an organization. Data subject requests can be extensive, confusing, and have plenty of requirements an organization needs to consider as they develop a data subject request policy and build the process.
What is a Data Subject Request?
Data subject requests (DSRs) and data subject access requests (DSARs) are at the centre of modern privacy laws. A data subject request is a request from an individual to an organization for accessing, modifying, or deleting the personal data that organization may hold about them. If you hear the term DSAR, it specifically refers to the access (download) request. Modern privacy regulations have privacy rights defined within the law, and puts the onus on each organization collecting personal data to fulfill these requests that an individual makes against their organization. Organizations must follow specific guidelines when it comes to fulfilling these requests, such as identify verification, fulfillment timelines, or what’s included in the response.
As an organization grows, so does this process: new team members joining the organization will add in new systems that collect personal data, sometimes without any notice or permission. This makes tracking down a user's data overwhelming, and hard to navigate.
What types of rights do individuals have across regulations?
As modern privacy laws are rapidly introduced around the world, they have slight differences in requirements for fulfilling data subject requests or privacy rights. Below is an example matrix of the different types of requests, rules, and what jurisdictions they may apply to.
| Request Type | What needs to be fulfilled | Jurisdictions |
|---|---|---|
Access or Download (also referred to as DSAR, Data Revelation, Data Portability, Data Export) | If an individual makes this request, an organization must provide a copy of their data in machine readable format. | Europe GDPR, California CCPA/CPRA, Virginia CDPA, Brazil LGPD, Canada CPPA, Colorado Privacy Act |
Data Deletion (also referred to as right to be forgotten, right to erasure) | If an individual makes this request, an organization must delete their personal data (within reason) from their systems and services. | Europe GDPR, California CCPA/CPRA, Virginia CDPA, Brazil LGPD, Canada CPPA, Colorado Privacy Act |
Opt-Out of Sale (also referred to as Do Not Sell) | If you “sell” personal data, an individual has the right to opt-out their information from being sold. This will apply to new and existing personal data collected. Important to note that CCPA has a broad definition of “sale”, that doesn’t include only monetary purposes. | California CCPA/CPRA |
Opt-Out of Processing | If an individual makes this request, you can still store their personal data, but you cannot process it. | Europe GDPR, Colorado Privacy Act |
Opt-Out of Decision Making | If an individual makes this request, you can no longer process their data through AI to make decisions. | Europe GDPR, California CPRA |
Update Inaccuracies | If an individual makes this request, you can update their personal data if it is inaccurate, or needs correction. | Europe GDPR, California CPRA, Virginia CDPA |
Book a demo today
Get a free, no-pressure demo of our software.
It’s important to note that these data subject requests or rights are context-specific. For example, there might be overarching laws that prevent you from completely fulfilling a data deletion request.
Does this seem like a burden to maintain long-term? Absolutely! And data subject requests must be fulfilled at no-cost. Certain regulations carve out expectations where if a user submits an excessive amount of requests, you could charge them, but this is regulation specific, and typically we’ve seen an allowance of 2 requests per year per individual, that must be no cost.
In recent years, the United States has been continuously introducing senate bills, and these requirements necessitate workflow changes. We’ve developed a matrix containing the different bills across each state, and the potential requirements being introduced.
Why do you need a DSR process?
Reason #1: Building Brand Trust
Consumers continue to become more privacy-aware, and a recent survey from Consumer Reports shows that 74% of Americans are concerned about the privacy of their personal data online, and 96% of Americans agree that more should be done by organizations to protect the privacy of consumers.
Allowing individuals to control their data is a great way for organizations to showcase their data practices, and that they can be trusted with data they collect. The concept of privacy rights is a drastic shift from recent years, where your users can now have ownership of the data that you collect about them.
Demonstrating a privacy posture is now becoming a consumer expectation. This means regardless of where your organization does business in the world, it is still proving to be highly beneficial to facilitate data subject requests for your users. Demonstrating these assurances shows that your company is worth trusting.
Reason #2: Compliance & Regulations
Modern privacy legislation has privacy rights embedded in the core. There have been significant fines around privacy rights in the GDPR. Our calculation shows there has been over $10M in fines since 2018 due to privacy right violations, alone. The majority of fines have resulted from failing to properly identify individuals, or not fulfilling requests within the required timeline. Further, we’ve seen around $300M worth of fines more broadly speaking, which equates to roughly 1.5 fines per day.
Guiding Principles for DSRs
Although there are plenty of regulations, both in effect and emerging, with data subject requests, there are some constant principles across all regulations that we’ve identified.
- Make it dead simple: Organizations should use clear, concise language when referring to data subject requests, and make them easy to access. Responses should be concise, and easy to understand with the appropriate language.
- Identity verification: Since DSRs are sensitive as you are often exchanging personal data, organizations must verify the identity of the requester. By verifying the identity of the requester, you avoid the potential leak of personal data to the wrong individual.
- Fulfill it promptly: Each privacy legislation has their own timelines for when you need to fulfill data subject requests. The tightest timeline we’ve seen to date is Brazil’s LGPD, which requires requests to be fulfilled within 15 days of receiving the request. This leaves very little time, as you need to verify their identity and gather the data to fulfill the request within this time. It’s why a guiding principle we recommend is to fulfill requests immediately.
- Privacy Ops should own this process: Failure to fulfill data subject requests can lead to massive penalties. For instance, non-compliance with California’s CCPA or Virginia’s CDPA data subject request requirements can result in $7500 per violation. With Europe’s GDPR, data subject request fines can reach €20 million or 4% of annual revenue, whichever is larger. This is why data subject requests should be owned by your privacy operations team. In smaller organizations, we do see customer service teams championing this process, but it’s still important that the privacy operations team still oversees it.
What are the primary steps to a DSR?
Although the privacy ops team should be owning the process, the task of fulfilling a data subject request often cuts across a few teams. The typical teams we see involved with data subject requests are legal/privacy teams and technical teams. This means that the workflow for DSRs must be cross-functional.
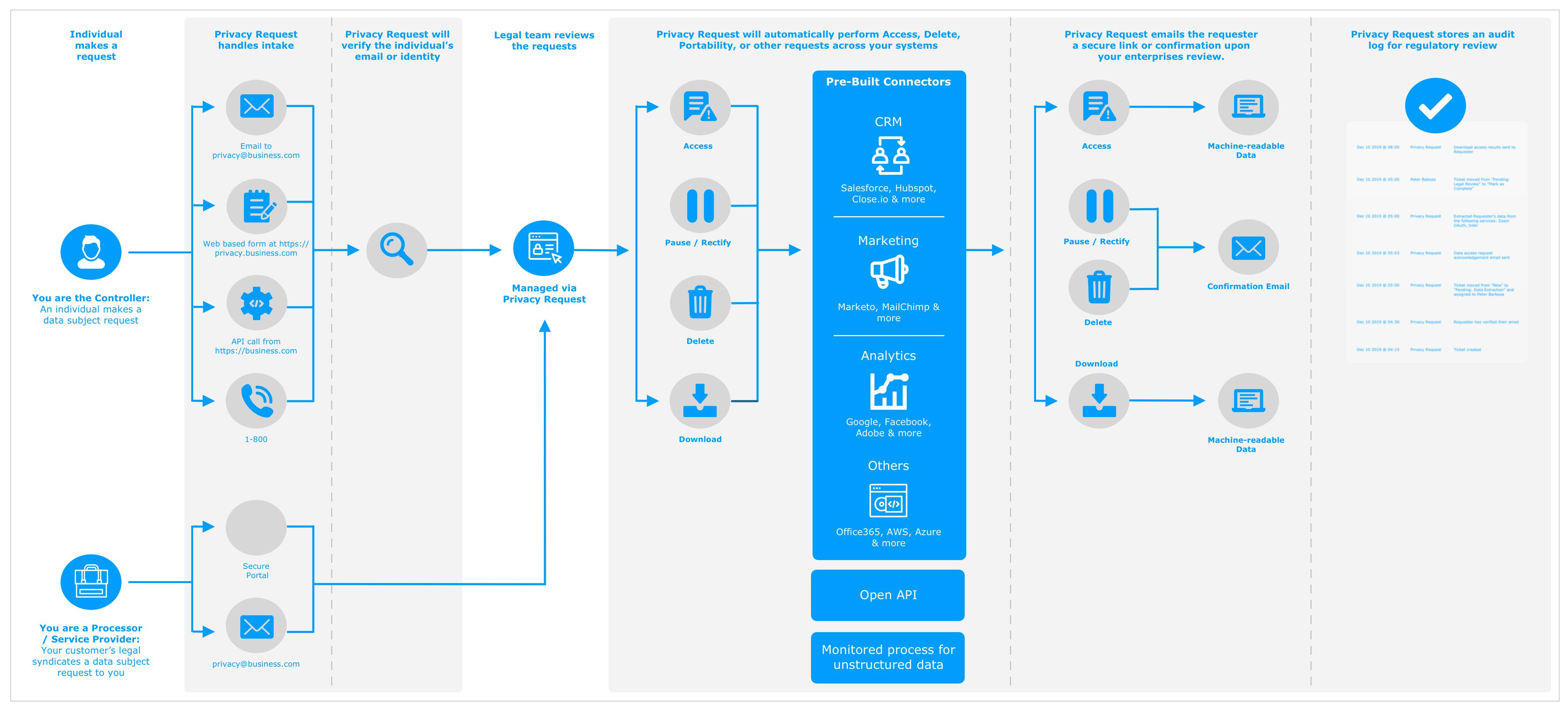
You could face a constant stream of these data subject requests if your organization operates around the globe. As such, it’s important your systems and teams are in sync to carry out this process, and understand what team owns what task.
There are 3 key steps to every DSR once it’s submitted.
Step 1: Verify the identity of the requester
There are multiple ways you can verify the identity of a requester. An easy way to do this is to ask the user for information that your organization uses to identify them. For example, if your organization relies on their email for managing their account, this could be sending an email to the requester to verify that the email provided is theirs. We’ve seen other methods such as security questions, or requesting a unique identification code, and matching it with other information provided. If your organization has a customer center online (that has a secure login only accessed by that individual), this could be a quick way to verify their identity.
Step 2: Identify places that the user's data may reside (including proprietary and third party systems).
You may have read our article on LinkedIn for building and documenting a data map. This is when your data map can not only help with demonstrating compliance, but also help identify the different data sources a user's data might exist. The above task might sound easy, but it can be a challenge in practice.
This also includes any cloud or SaaS tools that your organization might be paying for that include personal data (marketing tools like Salesforce, MailChimp). You will need to identify the internal business contacts who own these different systems and applications, and request that they help you fulfill the specific request.
Don’t forget about your home-brewed or proprietary systems that might have personal data. Each of these systems or databases might have their own unique structure to consider. In the context of data deletion, you will need to consider data integrity if a record is deleted.
As you may notice, providing a full picture back to the individual of their data requires a comprehensive data inventory. We strongly suggest referring back to our previous LinkedIn post on how to do this, or look into our DSR automation solution to help solve this. Having each team do this work on their own is often resource- and time-intensive, and might create a larger risk if teams don’t consider the timelines as per the regulations.
Step 3: Consolidate the relevant user data, and provide it in a machine readable format.
Lastly, you need to deliver an easy-to-read response. It’s important that your response is in the same language as the data subject.
In the context of a data download request, this can be very cumbersome. The goal of an access or download request is to provide the individual with a copy of their data, in machine-readable format. If you are pulling from IT systems and databases, you may notice that the exports contain internal field names. For example, your marketing system may output a field labeled “custom1”. It’s important to relabel these before sending the data back to the individual, so they understand what specific data that is being collected. Another common scenario we see is “shipping1” and “shipping2” fields, that are not properly labelled in a database. This means you will want to do a review of each data field, and re-label them before sending back the response. You want to relabel these to be simple, yet meaningful to the individual. Your technical teams may provide you a structured format of the data. A structured format could be a file type such as CSV, or JSON. While this is still valuable to the individual, we suggest providing a summary of this data in something like a PDF that is more user friendly.
For other requests such as a data deletion, or update personal data request, instead of delivering a copy of personal data, you will want to provide a confirmation that this has been executed or completed. We strongly recommend that you execute these requests with caution, as they often cannot be reversed. This could create errors or issues downstream with other vendors or applications that can break data integrity.
Other Key Considerations
Overarching laws and regulations
Your organization may be subject to other laws and regulations that could impact what data you need to retain, or what you share. It’s important to understand the scope of other laws you might need to consider (HI-TECH, HIPAA, GLBA, etc).
User Experience
We encourage a simple user experience for individuals that makes it easy to access their data. Some organizations often have different portals for data subject requests depending on the requester. Example, your employees might fill out a form on a company intranet, and customers might have an experience that can be accessed from your marketing website.
Opsware provides both of these methods. See the screenshot below of the “privacy center” we offer to organizations.
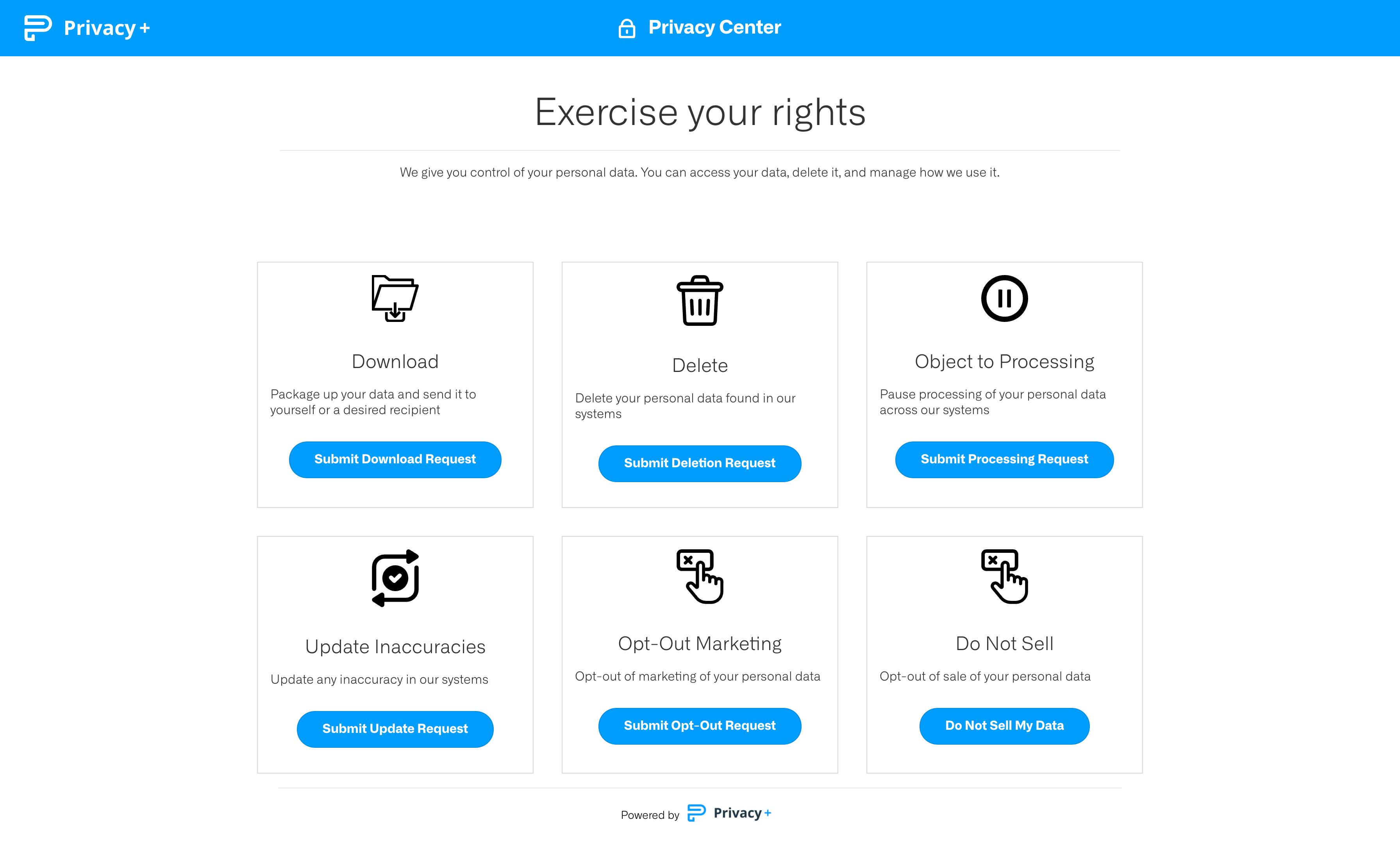
You will notice we make the requests easily accessible, with clear and concise language. It's important to collect only the minimum amount of information required to verify the user and fulfill the data subject request. You do not want to collect more information than you require. If you’re interested in providing this to your customers, don’t hesitate to reach out to us.
Automation
It can be overwhelming to keep track of the regulations around the globe, and what might impact your business, let alone fulfilling these data subject requests as per the requirements of each regulation.
This is when it’s best to look at data subject request automation solutions like Opsware. Opsware gives you an auditable trail of each request, and helps automate the necessary steps required to fulfill and complete a DSR in a compliant manner.
We help you develop best-in-class data subject request workflows as we discussed in this article. Making the entire process easy for anyone involved - including your internal team. Our DSR automation tool has pre-built connectors to cloud systems to help automate, and we can easily connect to your proprietary data systems in just a few minutes.
For your customers or employees, we provide a very easy to read package of their data and help remove the tedious work of legal reviews.
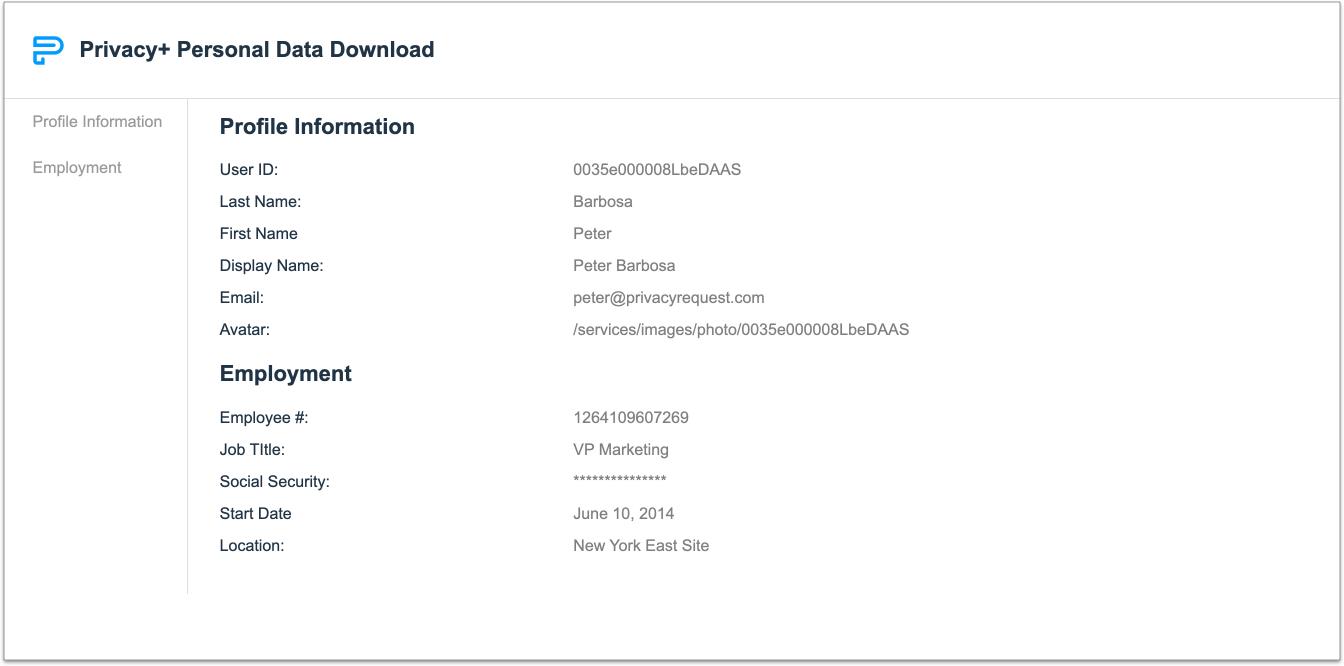
By automating, and having an auditable process, you can be confident in your data subject requests and not need to worry about the potential of fines and penalties.
We highly recommend speaking with your legal or privacy team before kicking off your data subject request workflow.
At Opsware, we also help organizations implement data subject request workflows and can provide consulting for how to develop this workflow internally.
Taking Control of Data Subject Requests
If you’re ready to implement a data subject request workflow, or want to take your existing workflow to the next level, don’t hesitate to reach out to us and see how we can help. We’re always happy to answer questions, or provide any insights on how to make this easy for you.
Peter Barbosa
PRIVACY